Last Updated: December 13th, 2024
Nodes
variety of types of entities
variety of properties per node
Edges
must be directed edges
variety of types of relationships
variety of properties per edge
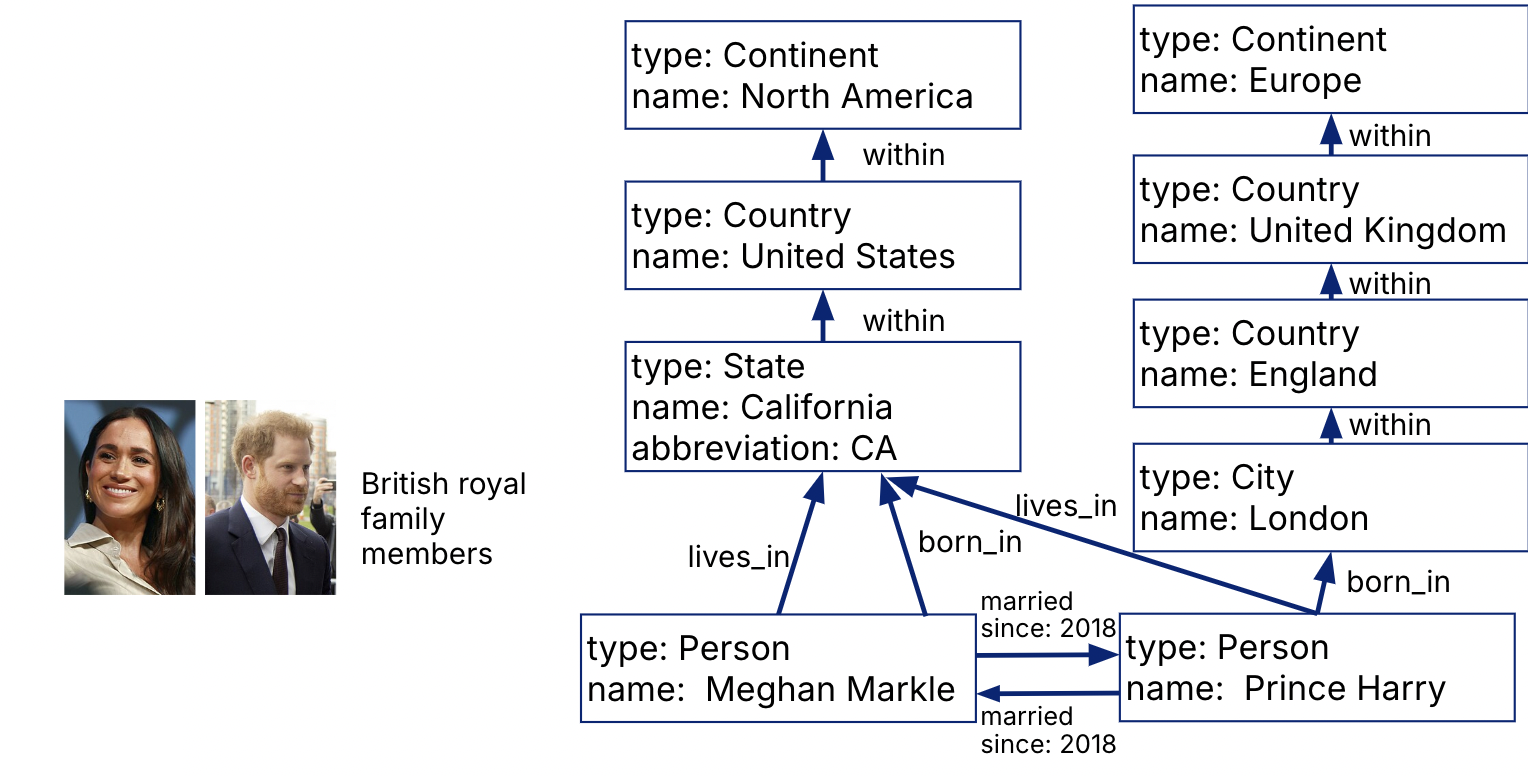
At the high level, just “two representations”: nodes and edges.
As opposed to a more restricted, multi-relational schema. In property graphs, node encompasses many entity types, edge encompasses many relation types.
Can be represented as just two relations in RDBMS
Easy support of graph expansion/evolution: Add new nodes, new edges, properties to existing nodes/edges
Easily supports graph traversal and path queries:
PathStart from any node, efficiently find incoming/outgoing edges, etc.
As opposed to pure JSON, where nested structure is difficult to query/manage
Flexible ordering/relationships creates more execution strategies
Property Graphs in RDBMSes¶
CREATE TABLE nodes
(node_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
type STRING,
properties JSON);
CREATE TABLE edges
(edge_id INTEGER
PRIMARY KEY,
head_id INTEGER
REFERENCES Nodes(node_id),
tail_id INTEGER
REFERENCES Nodes(node_id),
type STRING,
properties JSON);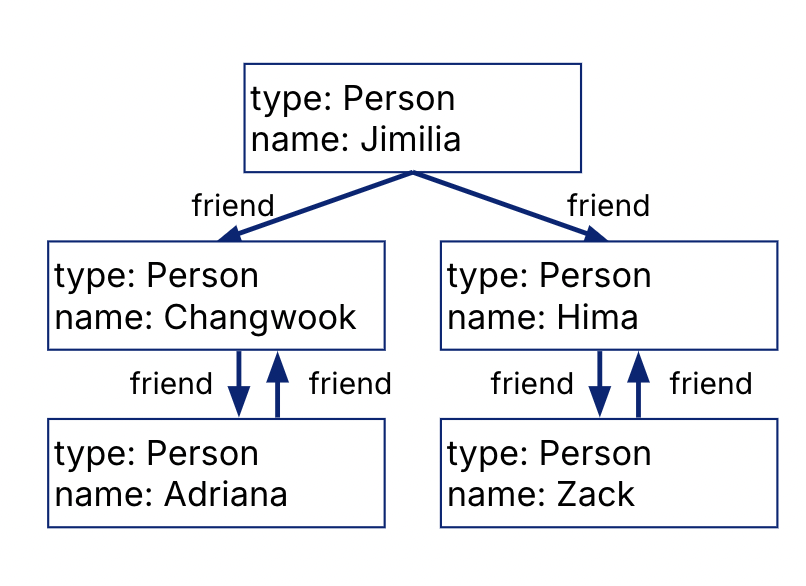
Path Traversal Queries in SQL¶
Suppose we want to find all the US locations in the graph database.
nodes(node_id, type, properties)edges(edge_id, head_id, tail_id, type, properties)
WITH RECURSIVE in_usa (node_id) AS (
( SELECT node_id
FROM nodes
WHERE properties->>'name' = 'United States'
) UNION (
SELECT tail_id
FROM edges
JOIN in_usa ON edges.head_id = in_usa.node_id
WHERE edges.type = 'within'
)
)
SELECT * FROM in_usa;Path traversals of graphs in SQL are achieved using recursive CTEs.
If we wanted rapid path traversal on incoming/outgoing edges, we could build additional indexes:
CREATE INDEX edge_tails
ON edges(tail_id);
CREATE INDEX edge_heads
ON edges(head_id);